Growth and Development MCQs
Dharmenedra Bansal
1. Which of the following explains the term economic growth?
a. Increase in per capita production
b. Increase in per capita real income
c. structural change in the economy
d. all the above are right✔
b. Increase in per capita real income
c. structural change in the economy
d. all the above are right✔
2. Economic development is characterized by
a. Structural change in the economy
b. Change in the occupational structure
c. Both a and b✔
d. None of the above
b. Change in the occupational structure
c. Both a and b✔
d. None of the above
3. Which of the following explains the term economic development?
a. Improvement in the technology involved
b. Improvement in production
c. Improvement in distribution system
d. All the above✔
b. Improvement in production
c. Improvement in distribution system
d. All the above✔
4. An underdeveloped economy is characterized by
a. High per capita real income
b. Large proportion of labor force in the tertiary sector
c. State of deprivation of large proportion of population✔
d. All the above
b. Large proportion of labor force in the tertiary sector
c. State of deprivation of large proportion of population✔
d. All the above
State of deprivation of large proportion of population
Underdeveloped countries face the problem of deprivation of large section of the population, low per capita real income etc.
5. Scarcity of capital , technological backwardness and unemployment are generally found in
a. Developed countries
b. Underdeveloped countries✔
c. Both
d. None of the above
b. Underdeveloped countries✔
c. Both
d. None of the above
6. Which of the following denotes an underdeveloped economy?
a. High level of inequalities
b. Low level of capital productivity
c. A relatively closed economy
d. All the above✔
b. Low level of capital productivity
c. A relatively closed economy
d. All the above✔
Other than the above features, there is High incidence of poverty, rapid population growth and technological backwardness too.
7. Capital formation in underdeveloped countries is a major bottleneck. The reason can be
a. Small size of market with no incentive for investment
b. Low level of income
c. Demonstration effect
d. All the above✔
b. Low level of income
c. Demonstration effect
d. All the above✔
8. Consider the following statements and identify the right ones.
i. Higher level of capital-output ratio indicates efficient use of capital.
ii. It reflects the productivity of capital in the economy
a. I only
b. ii only✔
c. both
d. none
b. ii only✔
c. both
d. none
COR refers to the number of units of capital required to produce one unit of output. A higher level of it means inefficient use of capital.
9. Consider the following statements and identify the right ones.
i. COR is relatively low in labour intensive sectors.
ii. COR will be high in capital intensive sectors
iii. Both✔
iv. None
ii. COR will be high in capital intensive sectors
iii. Both✔
iv. None
It is high in capital intensive industries because of more use of capital and timelag between investment and production.
10. Which of the following about strategy of balanced growth is right?
a. Simultaneous investment in all sectors✔
b. All sectors are independent.
c. Both
d. None
b. All sectors are independent.
c. Both
d. None
Simultaneous investment in all sectors.
The supporters of this theory argue that simultaneous investment in all the sectors will help in faster growth. It is based on the idea that all sectors are interlinked.
11.Which of the following had the approval of the classical economists (particularly J.S. Mill) as an aid to development?
A.Subsidizing the poor
B.Imposition of temporary duties on imports to develop particular industries✔
C.Regulation of activities of the rising business class
D.Appropriating a part of the national product by the government for unproductive uses
12.The capital-output ratio is determined by:
A.Sectoral allocation of capital
B.Level of economic activity
C.Human and natural resources
D.All of the above✔
13.Who formulated the theory of circular and cumulative causation which explains the perpetuation of underdevelopment through growing inequalities between developed and the underdeveloped countries?
A.Lewis
B.Gunnar Myrdal✔
C.Higgins
D.J.H.Boeke
14.Which of the following models uses three distinct concepts of stages of growth?
A.Ramsey model
B.Harrod model✔
C.Domar model
D.Lewis model
15.The classical theory of economic development is of relevance for the less developed countries today because it lays emphasis on:
A.Need for favourable institutional and social initiatives
B.Extension of markets
C.Capital accumulation
D.All of the above✔
16.Which growth model inspired the use of capital-output ratio for development planning?
A.The Harrod-Domar model✔
B.Solow's mode
C.Kaldor's model
D.Feldman's model
17.The second stage of the theory of demographic transition is characterised by:
A.High birth-rate and high death rate
B.High birth-rate and falling death-rate✔
C.Low birth-rate and low death-rate
D.falling birth rate and high death rate
18.According to the neo-classical theory, economic development is:
A.Gradual
B.Harmonious
C.Cumulative
D.All of the above✔
19.The capital-output ratio in a country during the different phases of growth:
A.Remains unchanged
B.Fluctuates widely
C.Changes within narrow limits✔
D.None
20.Which of the following concepts, which are now extensively used in growth economics, was first formulated by Keynes?
A.Marginal propensity to consume
B.Marginal propensity to save
C.Marginal efficiency of capital
D.All of the above✔
21.Unemployment created by some long-term change in demand or technological conditions in an economy is known as:
A.Frictional unemployment
B.Cyclical un-employment
C.Structural unemployment✔
D.Disguised unemployment
22.As an aid to development planning, much use is being made today of the input-output analysis. Who first used it?
A.H. Liebenstein
B.W.W.Leontief✔
C.W.A.Lewis
D.A.O.Hirshman
23.According to Keynesian economics, saving and investment are brought into equilibrium by variations in:
A.Income✔
B.Price
C.Consumption
D.Output
24.Arrange the following Rostow’s stages of economic growth in their proper sequence:
I, Traditional society;
II. Take-off stage;
III. Age of mass consumption;
IV. Drive to maturity
A.I, II, IV, III✔
B.I, II, III, IV
C.II, I, IV, III
D.II, I, III, IV
25.Balanced growth implies:
A.Simultaneous development of a variety of activities, which support one another✔
B.Equal allocation of resources to different sectors
C.Different sectors growing at their natural rates of growth
D.Uniform rate of growth of output over time
26.Which of the following is generally regarded as the true index of economic growth?
A.An increase in national income at constant prices during a year
B.A sustained increase in real per capita income✔
C.An increase in national income at current prices over time
D.An increase in national income along with a corresponding incease in population
27.Which of the following statements is not correct in the light of the Malthusian theory of growth?
A.Growth of income cannot take place on its own
B.Population tends to increase in response to rise in income
C.There can be no general glut or overproduction in the market✔
D.Excess savings on the part of capitalists is the cause of overproduction
28.The concept of economic growth is:
A.Identical with the concept of economic development
B.Narrower than the concept of economic development✔
C.Wider as compared to that of economic development
D.Unrelated to the concept of economic development
29.Which of the following statements is not in agreement with the Malthusian view on economic growth?
A.The process of economic growth is automatic✔
B.Deficiency in effective demand halts the growth process
C.Lasting equilibrium can only be at the subsistence level
D.Savings are desirable only upto the limit set by the existence of profitable opportunities for investment
30.Which of the following is not an indicator of economically underdeveloped countries?
A.Low per capita income
B.
High death-rate
C.Low proportion of labour force in the primary sector✔
D.High level of illiteracy
31.Which sector was emphasised most by Ricardo in the context of economic growth?
A.Trade
B.Industry
C.Agriculture✔
D.Services
32.The rate of growth of an economy mainly depends upon:
A.The rate of growth of the labour force
B.The proportion of national income saved and invested
C.The rate of technological improvements
D.All of the above
33.In the Ricardian scheme of things, savings are provided by:
A.Labourers
B.Capitalists✔
C.Landlords
D.Both (b) and (c)
34.Among the following determinants of growth, which is a non-economic factor?
A.Natural resources
B.Population growth
C.Favourable legislation✔
D.Capital accumulation
35.Whichone of the following, according to Ricardo, would form a bottleneck to economic growth?
A.Shortage of land✔
B.Rising rent
C.Shortage of gold and silver
D.Rising wage bills
36.Besides increase in output, economic development is concerned with:
A.Inputs and their efficiency
B.Equitable distribution of income
C.Life sustenance, self-esteem and freedom from want, ignorance and squalor
D.All of the above✔
37.Which one of the following statements is not in tune with the Ricardian theory of growth?
A.Rent tends to rise
B.Money wages tend to rise
C.Profits tend to fall
D.Profits tend to rise✔
38.The stationary state as envisaged by Adam Smith, is marked by:
A.Low rate of profit
B.Subsistence level wages
C.High rents
D.All of the above✔
39.Which one of the following is not an assumption of the Ricardian theory?
A.Rising real wages✔
B.Fixity of land
C.Operation of the law of diminishing returns
D.Perfect competition
40.Which of the following is inconsistent with Adam Smith’s theory of development?
A.Development process is cumulative in nature
B.There is no limit to the growth process✔
C.Capital accumulation and market extension are two prerequisites for output expansion
D.There should be no government interference in the working of the economy
41.What causes development in terms of Rostow’s theory?
A.Favourable propensities of people
B.Changing profile of leading sectors of the economy
C.A sharp rise in investment
D.All of the above✔
42.Which of the following is not correctly matched?
A.Big-push strategy: Paul N. Rosenstein- Rodan
B.Balanced growth theory: R. Nurkse✔
C.Development with unlimited supplies of labour: A-0. Hirschman
D.Critical minimum strategy: H. Uebenstein
43.J.F. Meade pointed out three principles means of growth. Which of the following is not on the list?
A.Growth of working population
B.Capital accumulation
C.Devaluation✔
D.Technical progress
44.Identify the country which was the first to move to the stage of high mass consumption:
A.UK
B.USA✔
C.Germany
D.France
45.If the capital-output ratio is 4:1 and the annual growth rate of population is 2.5%, what will be required rate of investment in the economy in order to achieve 3% growth per annum in per capita income?
A.30%✔
B.20%
C.15%
D.12%
46.The Harrod-Domar model is one of the well known models of growth. Which of the two authors of this model wrote earlier and in which year?
A.Domar in 1940
B.Harrood in 1939✔
C.Domar in 1946
D.Domar in 1948
47.The take off stage characterised by:
A.Rise in the rate of productive investment from 5% to over 10% of national income
B.Development of one or more substantial manufacturing sectors with a high growth rate
C.Quick emergence of a political, social and institutional framework to enable expansion in various fields
D.All of the above✔
48.With economic growth, the proportion of labour-force engaged in agriculture:
A.Increases
B.Decreases✔
C.Remains unaffected
D.Changes in an uncertain manner
49.Which of the following models formed the basis of India’s Second Five Year Plan?
A.Harrod-Domar model
B.Raj-Sen model
C.Cambridge model
D.Mahalanobis model✔
50.Under the ‘big-push’ strategy of development, large investments are to be directed towards:
A.Agriculture
B.Industry✔
C.Power
D.Transport
51.A strategy of heavy industry is sometimes preferred for a developing economy because it can:
A.Generate employment opportunities on a large scale
B.Provide a strong base for rapid industrialisation✔
C.Contain inflationary pressures
D.Meet deficits in balance of payments in the short-run
52.Which of the following models makes the assumption of constant saving-income ratio?
A.Kaldor model
B.Leontief model
C.Harrod-Domar model✔
D.Joan Robinson model
53.The basic logic behind the ‘big-push’ strategy of development is related to:
A.Internal economies
B.External economies✔
C.An optimum combination
D.Both (a) and (b)
54.In which sphere are shadow prices particularly useful?
A.Project evaluation and cost-benefit analyses✔
B.calculation of surplus value
C.Sales policy of firms
D.Consumers equilibrium
55.Identify the model which is concerned with the ‘golden age’ equilibrium:
A.Kaldor model
B.Joan Robinson model✔
C.Keynesian model
D.Domar model
56. The additional capital used per unit of additional production is called
a. Induced investment
b. Autonomous investment
c. Incremental COR✔
d. None of the above
COR refers to the number of units of capital required to produce one unit of output.
57.Economic growth in India will happen necessarily if there is
a. Population growth
b. Capital formation✔
c. Technical progress in the global economy
d. All the above
Capital formation refers to investment in tools, machinery, buildings etc.
58.Inclusive governance includes
a. Allowing NBFCs to do banking
b. Increase government spending on health
c. Strengthening mid-day meals scheme
d. All the above✔
Inclusive governance denotes inclusion of schemes and other measures for benefit of all the sections of the society.
59.Which of the following denotes business activity at high level with increasing output and income?
a. Boom✔
b. Recession
c. Depression
d. Recovery
Boom, recession, depression and recovery are the phases of a business cycle.
60.The phase of gradual fall in income, output and employment is
a. Boom
b. Recession✔
c. Depression
d. Recovery
Boom, recession, depression and recovery are the phases of a business cycle. In this phase, business activity is in low gear.
A.Subsidizing the poor
B.Imposition of temporary duties on imports to develop particular industries✔
C.Regulation of activities of the rising business class
D.Appropriating a part of the national product by the government for unproductive uses
12.The capital-output ratio is determined by:
A.Sectoral allocation of capital
B.Level of economic activity
C.Human and natural resources
D.All of the above✔
13.Who formulated the theory of circular and cumulative causation which explains the perpetuation of underdevelopment through growing inequalities between developed and the underdeveloped countries?
A.Lewis
B.Gunnar Myrdal✔
C.Higgins
D.J.H.Boeke
14.Which of the following models uses three distinct concepts of stages of growth?
A.Ramsey model
B.Harrod model✔
C.Domar model
D.Lewis model
15.The classical theory of economic development is of relevance for the less developed countries today because it lays emphasis on:
A.Need for favourable institutional and social initiatives
B.Extension of markets
C.Capital accumulation
D.All of the above✔
16.Which growth model inspired the use of capital-output ratio for development planning?
A.The Harrod-Domar model✔
B.Solow's mode
C.Kaldor's model
D.Feldman's model
17.The second stage of the theory of demographic transition is characterised by:
A.High birth-rate and high death rate
B.High birth-rate and falling death-rate✔
C.Low birth-rate and low death-rate
D.falling birth rate and high death rate
18.According to the neo-classical theory, economic development is:
A.Gradual
B.Harmonious
C.Cumulative
D.All of the above✔
19.The capital-output ratio in a country during the different phases of growth:
A.Remains unchanged
B.Fluctuates widely
C.Changes within narrow limits✔
D.None
20.Which of the following concepts, which are now extensively used in growth economics, was first formulated by Keynes?
A.Marginal propensity to consume
B.Marginal propensity to save
C.Marginal efficiency of capital
D.All of the above✔
21.Unemployment created by some long-term change in demand or technological conditions in an economy is known as:
A.Frictional unemployment
B.Cyclical un-employment
C.Structural unemployment✔
D.Disguised unemployment
22.As an aid to development planning, much use is being made today of the input-output analysis. Who first used it?
A.H. Liebenstein
B.W.W.Leontief✔
C.W.A.Lewis
D.A.O.Hirshman
23.According to Keynesian economics, saving and investment are brought into equilibrium by variations in:
A.Income✔
B.Price
C.Consumption
D.Output
24.Arrange the following Rostow’s stages of economic growth in their proper sequence:
I, Traditional society;
II. Take-off stage;
III. Age of mass consumption;
IV. Drive to maturity
A.I, II, IV, III✔
B.I, II, III, IV
C.II, I, IV, III
D.II, I, III, IV
25.Balanced growth implies:
A.Simultaneous development of a variety of activities, which support one another✔
B.Equal allocation of resources to different sectors
C.Different sectors growing at their natural rates of growth
D.Uniform rate of growth of output over time
26.Which of the following is generally regarded as the true index of economic growth?
A.An increase in national income at constant prices during a year
B.A sustained increase in real per capita income✔
C.An increase in national income at current prices over time
D.An increase in national income along with a corresponding incease in population
27.Which of the following statements is not correct in the light of the Malthusian theory of growth?
A.Growth of income cannot take place on its own
B.Population tends to increase in response to rise in income
C.There can be no general glut or overproduction in the market✔
D.Excess savings on the part of capitalists is the cause of overproduction
28.The concept of economic growth is:
A.Identical with the concept of economic development
B.Narrower than the concept of economic development✔
C.Wider as compared to that of economic development
D.Unrelated to the concept of economic development
29.Which of the following statements is not in agreement with the Malthusian view on economic growth?
A.The process of economic growth is automatic✔
B.Deficiency in effective demand halts the growth process
C.Lasting equilibrium can only be at the subsistence level
D.Savings are desirable only upto the limit set by the existence of profitable opportunities for investment
30.Which of the following is not an indicator of economically underdeveloped countries?
A.Low per capita income
B.
High death-rate
C.Low proportion of labour force in the primary sector✔
D.High level of illiteracy
31.Which sector was emphasised most by Ricardo in the context of economic growth?
A.Trade
B.Industry
C.Agriculture✔
D.Services
32.The rate of growth of an economy mainly depends upon:
A.The rate of growth of the labour force
B.The proportion of national income saved and invested
C.The rate of technological improvements
D.All of the above
33.In the Ricardian scheme of things, savings are provided by:
A.Labourers
B.Capitalists✔
C.Landlords
D.Both (b) and (c)
34.Among the following determinants of growth, which is a non-economic factor?
A.Natural resources
B.Population growth
C.Favourable legislation✔
D.Capital accumulation
35.Whichone of the following, according to Ricardo, would form a bottleneck to economic growth?
A.Shortage of land✔
B.Rising rent
C.Shortage of gold and silver
D.Rising wage bills
36.Besides increase in output, economic development is concerned with:
A.Inputs and their efficiency
B.Equitable distribution of income
C.Life sustenance, self-esteem and freedom from want, ignorance and squalor
D.All of the above✔
37.Which one of the following statements is not in tune with the Ricardian theory of growth?
A.Rent tends to rise
B.Money wages tend to rise
C.Profits tend to fall
D.Profits tend to rise✔
38.The stationary state as envisaged by Adam Smith, is marked by:
A.Low rate of profit
B.Subsistence level wages
C.High rents
D.All of the above✔
39.Which one of the following is not an assumption of the Ricardian theory?
A.Rising real wages✔
B.Fixity of land
C.Operation of the law of diminishing returns
D.Perfect competition
40.Which of the following is inconsistent with Adam Smith’s theory of development?
A.Development process is cumulative in nature
B.There is no limit to the growth process✔
C.Capital accumulation and market extension are two prerequisites for output expansion
D.There should be no government interference in the working of the economy
41.What causes development in terms of Rostow’s theory?
A.Favourable propensities of people
B.Changing profile of leading sectors of the economy
C.A sharp rise in investment
D.All of the above✔
42.Which of the following is not correctly matched?
A.Big-push strategy: Paul N. Rosenstein- Rodan
B.Balanced growth theory: R. Nurkse✔
C.Development with unlimited supplies of labour: A-0. Hirschman
D.Critical minimum strategy: H. Uebenstein
43.J.F. Meade pointed out three principles means of growth. Which of the following is not on the list?
A.Growth of working population
B.Capital accumulation
C.Devaluation✔
D.Technical progress
44.Identify the country which was the first to move to the stage of high mass consumption:
A.UK
B.USA✔
C.Germany
D.France
45.If the capital-output ratio is 4:1 and the annual growth rate of population is 2.5%, what will be required rate of investment in the economy in order to achieve 3% growth per annum in per capita income?
A.30%✔
B.20%
C.15%
D.12%
46.The Harrod-Domar model is one of the well known models of growth. Which of the two authors of this model wrote earlier and in which year?
A.Domar in 1940
B.Harrood in 1939✔
C.Domar in 1946
D.Domar in 1948
47.The take off stage characterised by:
A.Rise in the rate of productive investment from 5% to over 10% of national income
B.Development of one or more substantial manufacturing sectors with a high growth rate
C.Quick emergence of a political, social and institutional framework to enable expansion in various fields
D.All of the above✔
48.With economic growth, the proportion of labour-force engaged in agriculture:
A.Increases
B.Decreases✔
C.Remains unaffected
D.Changes in an uncertain manner
49.Which of the following models formed the basis of India’s Second Five Year Plan?
A.Harrod-Domar model
B.Raj-Sen model
C.Cambridge model
D.Mahalanobis model✔
50.Under the ‘big-push’ strategy of development, large investments are to be directed towards:
A.Agriculture
B.Industry✔
C.Power
D.Transport
51.A strategy of heavy industry is sometimes preferred for a developing economy because it can:
A.Generate employment opportunities on a large scale
B.Provide a strong base for rapid industrialisation✔
C.Contain inflationary pressures
D.Meet deficits in balance of payments in the short-run
52.Which of the following models makes the assumption of constant saving-income ratio?
A.Kaldor model
B.Leontief model
C.Harrod-Domar model✔
D.Joan Robinson model
53.The basic logic behind the ‘big-push’ strategy of development is related to:
A.Internal economies
B.External economies✔
C.An optimum combination
D.Both (a) and (b)
54.In which sphere are shadow prices particularly useful?
A.Project evaluation and cost-benefit analyses✔
B.calculation of surplus value
C.Sales policy of firms
D.Consumers equilibrium
55.Identify the model which is concerned with the ‘golden age’ equilibrium:
A.Kaldor model
B.Joan Robinson model✔
C.Keynesian model
D.Domar model
56. The additional capital used per unit of additional production is called
a. Induced investment
b. Autonomous investment
c. Incremental COR✔
d. None of the above
COR refers to the number of units of capital required to produce one unit of output.
57.Economic growth in India will happen necessarily if there is
a. Population growth
b. Capital formation✔
c. Technical progress in the global economy
d. All the above
Capital formation refers to investment in tools, machinery, buildings etc.
58.Inclusive governance includes
a. Allowing NBFCs to do banking
b. Increase government spending on health
c. Strengthening mid-day meals scheme
d. All the above✔
Inclusive governance denotes inclusion of schemes and other measures for benefit of all the sections of the society.
59.Which of the following denotes business activity at high level with increasing output and income?
a. Boom✔
b. Recession
c. Depression
d. Recovery
Boom, recession, depression and recovery are the phases of a business cycle.
60.The phase of gradual fall in income, output and employment is
a. Boom
b. Recession✔
c. Depression
d. Recovery
Boom, recession, depression and recovery are the phases of a business cycle. In this phase, business activity is in low gear.

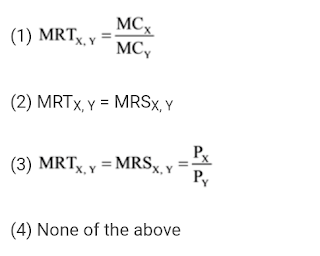
42 is wrong
ReplyDeleteRight answer is c
Can you explain Q and answer of net with detail explanation
ReplyDeleteThanks but 42 is wrong
ReplyDelete